Getting started with IOTEAM Dusty breakout
Overview
Dusty is a fully SmartMesh IP capable module commercialized by IOTEAM (http://ioteam.strikingly.com).
IOTEAM sells two versions of the Dusty:
- with a u.Fl connector to allow you to connect an external antenna
- with an on-board PCB antenna
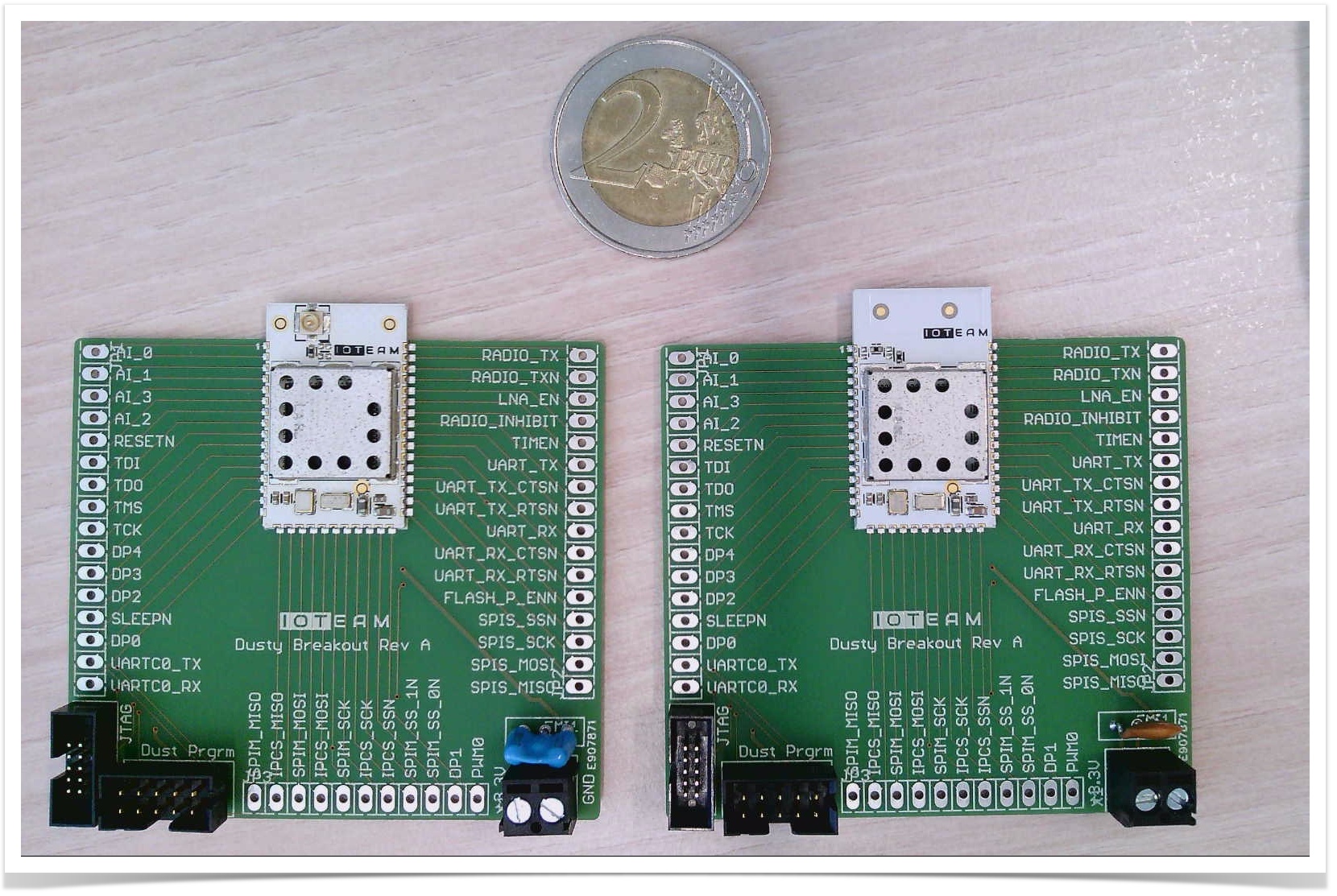
While you can buy just the module, for testing and prototyping, IOTEAM can ship you the module mounted on a breakout board, as shown below.
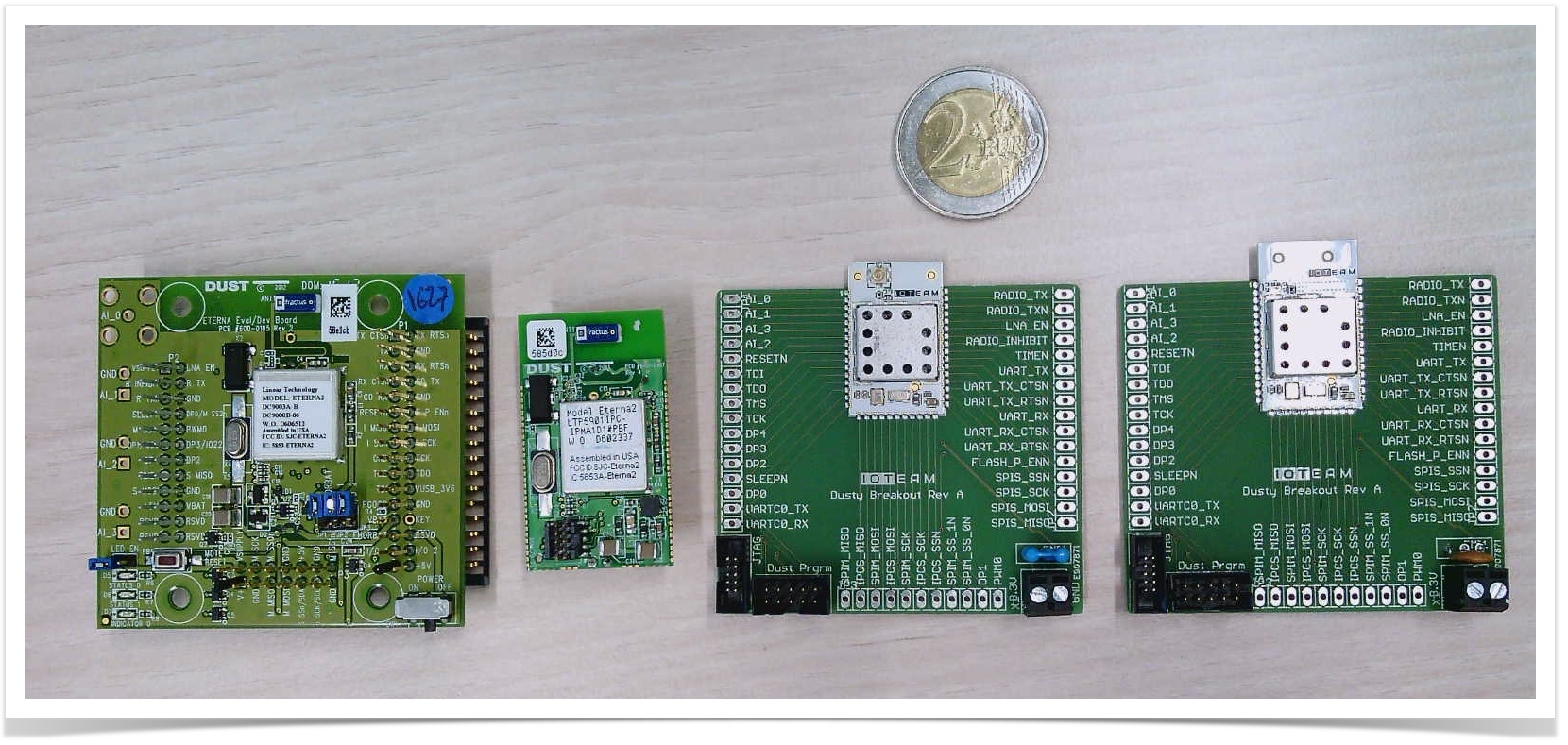
The Dusty is smaller than the motes and modules manufactured by Analog Devices:
In the picture above, from left to right:
- the DC9003 SmartMesh IP Eval/Dev Mote (http://www.linear.com/solutions/3106), manufactured by Analog Devices
- the LTP5901 SmartMesh IP Wireless 802.15.4e PCBA Module (http://www.linear.com/product/LTP5901-IPM), manufactured by Analog Devices
- two Dusty motes on their breakout boards, one with a u.Fl connector, the other with a PCB antenna
The Dusty mote features exactly the same LTC5800 chip, and is functionally identical to the LTP5901. This means that the Dusty mote, although it has a smaller footprint, behaves exactly the same. It is possible to build networks with a combination of Dusty and non-Dusty SmartMesh IP devices.
Any Dusty module can be programmed either as a manager or a mote. The modules come pre-programmed as either mote or manager according to your order, but you can easily reprogram them.
Powering the Dusty breakout
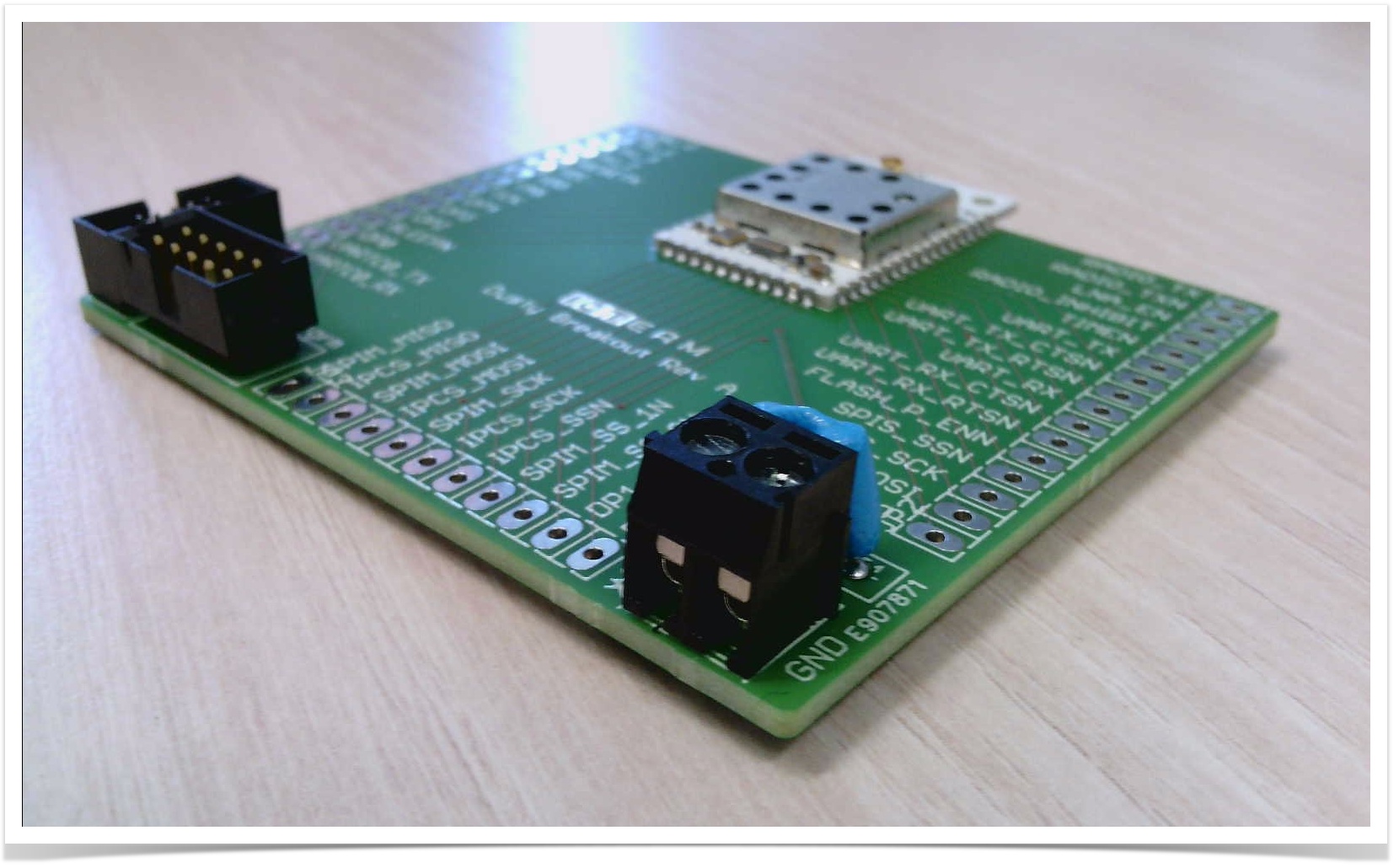
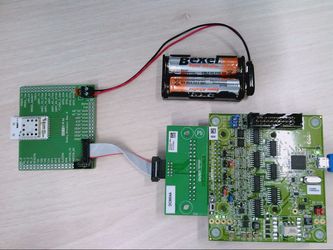
The Dusty breakout board comes with a very handy connector with 2 screw terminals, ideal for connecting a battery pack or any 3.3V external power source.
Just connecting the battery pack is enough to power the mote, no need to switch anything else on or off.
Accessing the CLI and API Serial Interfaces
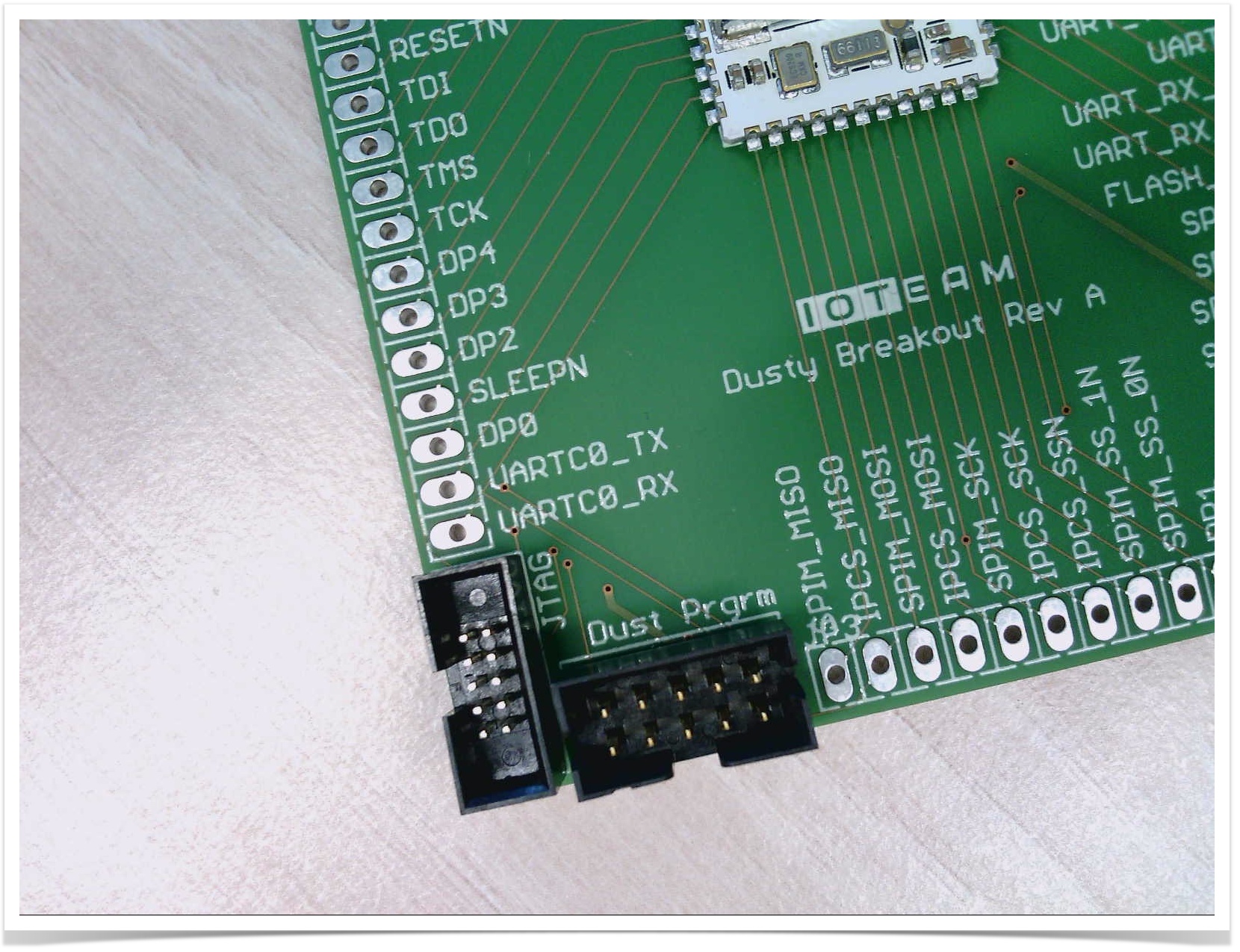
The Dusty breakout comes with the standard 10-pin Dust programming header ("Dust Prgrm" on the silkscreen).
This allows you to use the standard Dust interface boards and programmers to connect to Dusty:
| DC9010B Eterna Serial Programmer | using a DC9006A+DC9904A combo |
|---|
Both options depicted above are equivalent.
Through the programmer or the interface card, you are able to:
- access the CLI serial interface of Dusty
- access the API serial interface of Dusty
- re-flash Dusty with different firmware
Firing up the Mote
By default, the mote is in slave mode. If you want the mote to join a manager automatically (i.e. without using an external micro-controller), you can switch it to "master" mode:
> set mode master > reset
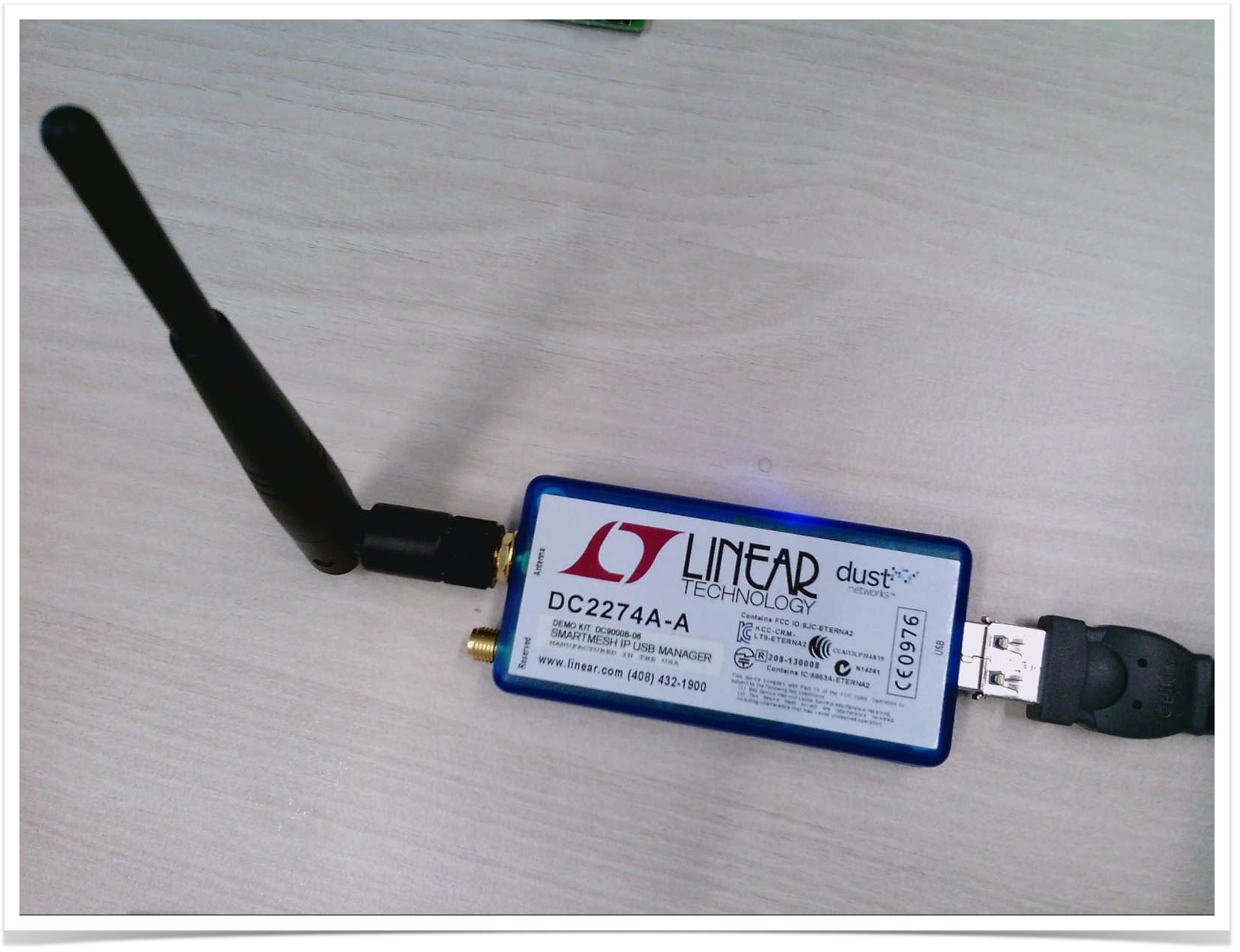
During this step, I use a DC2274 board as a manager, to verify the Dusty mote connects to it.
After the mote has reset, you can see it joining the manager:
> SmartMesh IP mote, ver 1.3.3.1 (0x40100) 5010 : Joining 5355 : Connected 11745 : Active
At the time of writing, the Dusty ships with IP mote 1.3.3.1 firmware:
> info IP Mote: 1.3.3.1 Join state: Complete Bandwidth Allocated: 8418 Serial mode: n/a Serial Baud Rate: n/a Radio Test: off
You can see the mote's (unique) MAC address by typing the following command:
> minfo Net stack v1.2.4.1 state: Oper mac: 00:17:0d:00:00:59:53:7a moteid: 2 netid: 1229 blSwVer: 15 ldrSwVer: 1.0.3.12 UTC time: 1025665345:237318 reset st: 40100
On the manager side, you can see that the mote has joined:
> login user
> sm
MAC MoteId State Nbrs Links Joins Age StateTime
00-17-0D-00-00-30-5D-39 1 Oper 1 21 1 0 0-00:00:32
00-17-0D-00-00-59-53-7A 2 Oper 1 9 1 6 0-00:00:10
Number of motes (max 101): Total 2, Live 2, Joining 0
You can ping your mote from the manager:
> ping 2 Sending ping request to mote 2 > Ping response from mote 2, time=1495 msec v=3062 t=26
Firing up the Manager
The difference between a manager and a mote is just the firmware. Their hardware is otherwise entirely equivalent. In particular, you power and connect to the board the same way.
At the time of writing, the Dusty comes with manager firmware version 1.2.4.1.
> login user > show ver SmartMesh IP Manager ver 1.2.4.1.
Because the Dusty breakout does not come with external memory, you can connect at most 32 motes to it (the "maxmotes" field below includes 32 motes and 1 manager).
The pins to connect external memory are present on the Dusty, so it's possible to build a board with a Dusty and external memory to be able to handle up to 100 motes.
> show config netid = 1229 txpower = 8 frprofile = 1 maxmotes = 33 basebw = 9000 dnfr_mult = 1 numparents = 2 cca = 0 channellist = 00:00:7f:ff autostart = 1 locmode = 0 bbmode = 0 bbsize = 1 license = 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 ip6prefix = fe:80:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 ip6mask = ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 radiotest = 0 bwmult = 300 onechannel = 255
setup
I have 13 additional non-Dusty SmartMesh IP motes running in master mode for the following step.
You can see that 13 motes, with MoteIds 2 through 14, have joined the manager (MoteId 1):
> sm
MAC MoteId State Nbrs Links Joins Age StateTime
00-17-0D-00-00-59-54-44 1 Oper 12 33 1 0 0-00:38:28
00-17-0D-00-00-38-03-D9 2 Oper 4 13 1 7 0-00:37:40
00-17-0D-00-00-38-03-87 3 Oper 3 11 1 3 0-00:23:47
00-17-0D-00-00-38-05-E9 4 Oper 4 12 1 16 0-00:20:28
00-17-0D-00-00-38-06-67 5 Oper 4 12 1 23 0-00:18:57
00-17-0D-00-00-38-07-18 6 Oper 3 11 1 1 0-00:18:08
00-17-0D-00-00-38-07-0C 7 Oper 2 10 1 28 0-00:11:57
00-17-0D-00-00-38-04-25 8 Oper 2 10 1 25 0-00:04:59
00-17-0D-00-00-38-06-6A 9 Oper 4 12 1 22 0-00:07:32
00-17-0D-00-00-38-06-D6 10 Oper 3 11 1 22 0-00:04:48
00-17-0D-00-00-38-05-F1 11 Oper 2 10 1 29 0-00:03:41
00-17-0D-00-00-38-03-69 12 Oper 3 11 1 2 0-00:04:47
00-17-0D-00-00-38-06-45 13 Oper 2 10 1 1 0-00:03:35
00-17-0D-00-00-38-00-63 14 Oper 2 9 1 27 0-00:03:08
Number of motes (max 33): Total 14, Live 14, Joining 0