Publish to Watson IoT Quickstart
SmartMesh IP mesh networks and and IBM Watson IoT are perfectly complementary. Sending data gathered by a SmartMesh IP mote into the Watson IoT platform is a breeze, as you will see in this recipe.
Overview
Create your network
We assume you have a DC9000B SmartMesh IP starter kit
There are many many things you can do with this kit, including connecting external sensors, reprogramming the motes, driving the motes from an external micro-controller, etc. In this recipe, we assume you are using an out-of-the-box kit, in which nodes are running the default firmware in master mode.
In this mode, each mote publishes a temperature reading every 30s. This is what we will publish to Watson IoT Quickstart.
Plug the manager into your computer's USB board and its blue LED switches on
When you plug the manager into your computer, 4 serial ports appear on your computer. If you're using Windows, they are listed in your Device Manager.
Note the number of the 4th port in the list, in my case "COM13".
Switch on at least one mote, two green LEDs are steady-on when the mote has successfully joined the network and is publishing data:
The LEDs are only active when the blue "LED EN" jumper is placed, as in the picture above.
Run the software
On your computer, you will need to run two programs: JsonServer and Node-RED
JsonServer
JsonServer is a program developed by the DustCloud community and part of the SmartMesh SDK.
It connects to your SmartMesh IP manager and opens an HTTP JSON interface that Node-RED can connect to.
Download the latest release of the SmartMesh SDK at https://github.com/dustcloud/smartmeshsdk/releases
There are several ways of running the SmartMesh SDK, depending on your operating system. On my Windows computer, the quickest way is to download the pre-compiled binaries:
Unzip the folder, and double-click on
SmartMeshSDK-1.1.1.0-win\win\JsonServer.exe.You can of course also download the (Python) source code and run that. This is documented at SmartMesh SDK.
- Run the application
Node-RED
- First, install Node.js. There a number of options. On my Windows machine, it just means downloading an installer and clicking through the default installation options.
- You can verify Node.js is installed by entering the following command (
npmis the "node package manager", part of Node.js)
C:\Users\twatteyne>npm --version 2.15.9
- You install Node-RED through
npm:
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
- Finally, you can start Node-RED:
C:\Users\twatteyne>node-red Welcome to Node-RED =================== 1 Sep 15:02:04 - [info] Node-RED version: v0.14.6 1 Sep 15:02:04 - [info] Node.js version: v4.5.0 1 Sep 15:02:04 - [info] Windows_NT 6.1.7601 x64 LE 1 Sep 15:02:04 - [info] Loading palette nodes 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [warn] ------------------------------------------------------ 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [warn] [rpi-gpio] Info : Ignoring Raspberry Pi specific node 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [warn] [tail] Not currently supported on Windows. 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [warn] ------------------------------------------------------ 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] Settings file : C:\Users\twatteyne\AppData\Roaming\npm\ node_modules\node-red\settings.js 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] User directory : \Users\twatteyne\.node-red 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] Flows file : \Users\twatteyne\.node-red\flows_HDC_SW 01.json 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] Creating new flow file 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] Starting flows 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] Started flows 1 Sep 15:02:05 - [info] Server now running at http://127.0.0.1:1880/
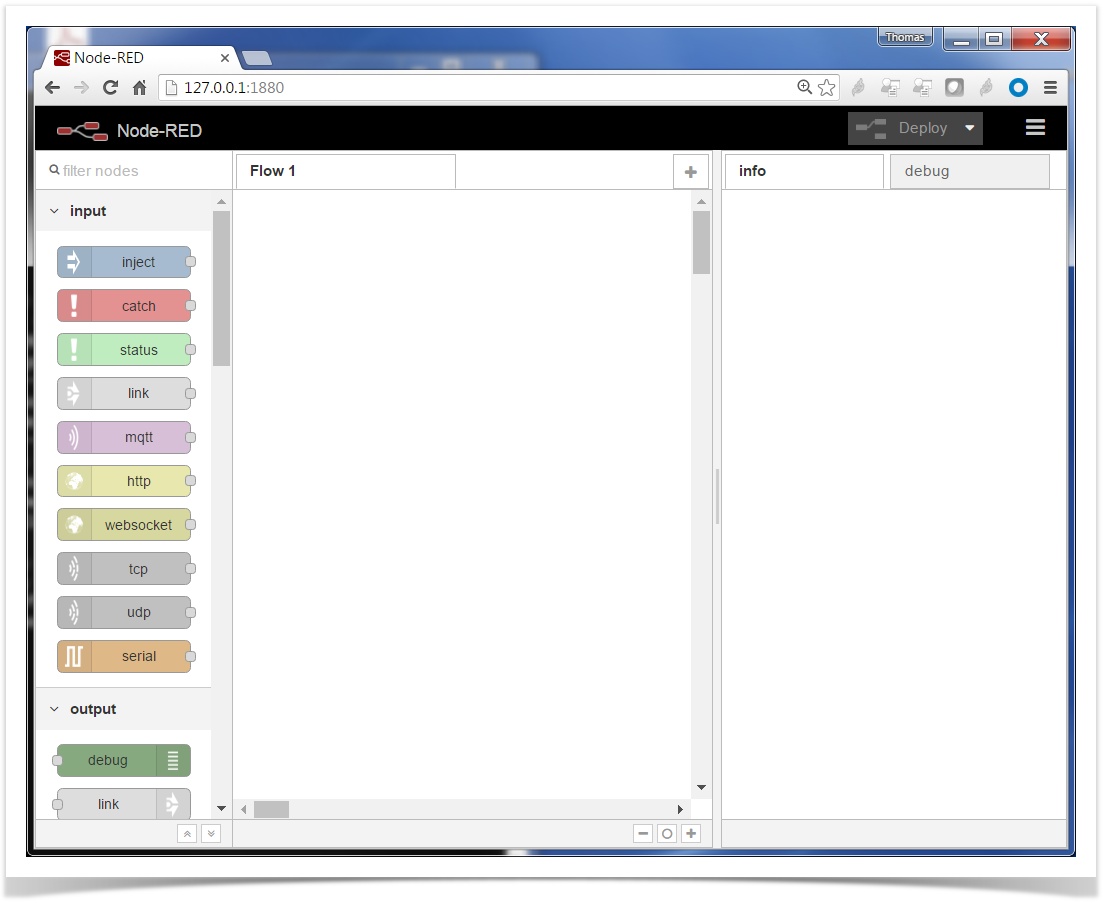
Point your browser to http://localhost:1880/ to see the Node-RED web interface:
Geeky details
As you can see from the URL above, the Node-RED application starts a web server which listens on port 1880.
Following the excellent Getting Started guide if you want to learn more about Node-RED.
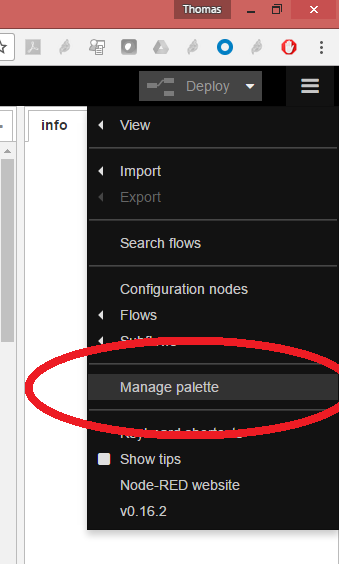
- use the hamburger menu on the upper-right and select "Manage palette"
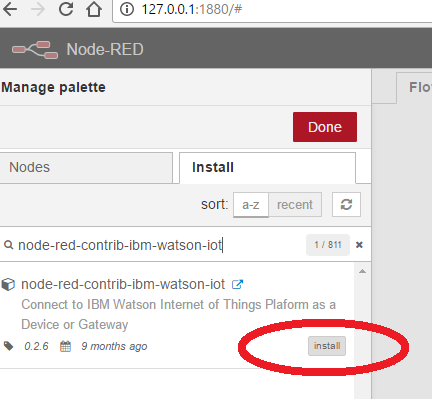
- search for "node-red-contrib-ibm-watson-iot" and install the additional palette
When am I done?
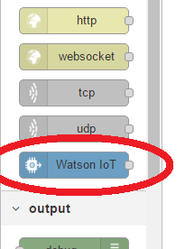
Open http://127.0.0.1:1880/ and make sure you see the Watson IoT nodes:
Publish to Watson IoT Quickstart
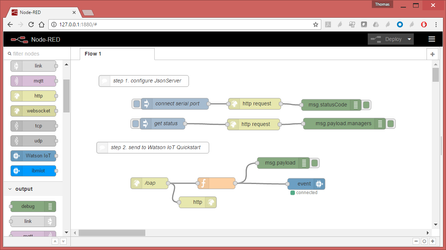
- Copy the following Node-RED flow into Node-RED:
JSON version of the flow
https://gist.github.com/twatteynelinear/9626af15ec56cf661ffe70734d3b11e0/raw/
To import the flow above in your Node-RED instance:
- click on the lab, and copy the entire contents of the file you just opened (Ctrl+C)
- in your Node-RED editor, on the hamburger menu on the upper right, select "Import" > "Clipboard"
- paste the string (Ctrl+V) and click "Import"
- activate the flow by clicking on the "Deploy" button
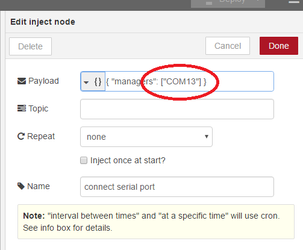
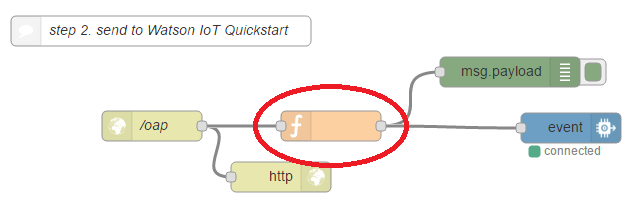
- Double-click on "connect serial port" and change "COM13" by the name of the serial port you noted above
- Click the Deploy button on Node-RED
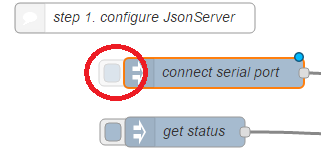
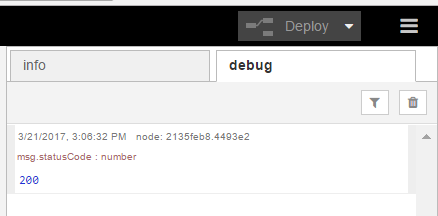
- Click on the left of the "connect serial port" widget
Make sure the debug tab on the right contains "200"
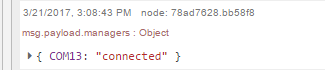
- Click on the left of the "get status" widget
Make sure the debug tab on the right contains "connected"
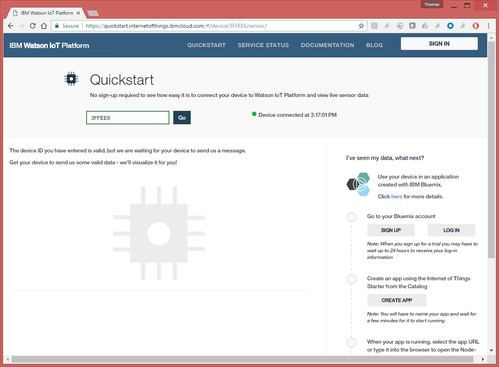
Choose any one of your motes, and read its label, in my case "3FFEE6"
What's that?
The label contains the unique identifier of the mote.
- In Node-RED, double-click on the function widget
- Replace "3FFEE6" by what you have on your label and click Done
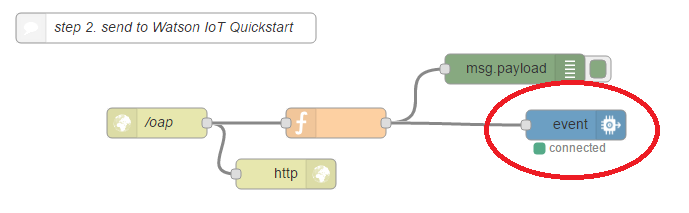
- Double-click on the event widget
- Change the Quickstart Id by your mote's identifier, and click Done
- Click Deploy
- Go to https://quickstart.internetofthings.ibmcloud.com
- check the box to accept the terms and conditions
- enter the identifier of your mote and press Go
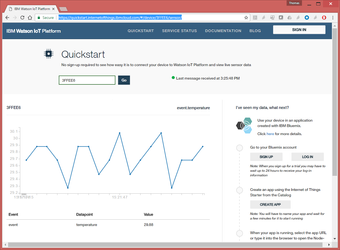
- You start by seeing an empty screen, this is normal as the mote only publishes every 30s
- Every 30s, a new datapoint plots live
You can see the same data on different devices, just go to https://quickstart.internetofthings.ibmcloud.com and enter the identifier of your board.
Where next?
We hope to have convinced you of how easy it is to send data from your SmartMesh IP to IBM Watson IoT. We have obviously only scratched the surface of what's possible.
Things you can do with your SmartMesh IP motes
- connect external sensors
- connect external actuators
- reprogram motes using the On-Chip SDK
- etc.
Things you can do with IBM Watson IoT
- create a your own Watson IoT instance (not the Quickstart) and send data in a quick and secure way into IBM Bluemix
- start other IBM Bluemix services and applications to store, analyze and visualize your SmartMesh IP network and the data it produces
- etc.