/
Develop
Develop
The SmartMesh SDK consists of three layers:
- The SmartMeshSDK layer provides a collection of ApiDefinitions and ApiConnectors:
- an ApiDefinition defines the commands, responses and notification of a given API, as well as the functions to manipulate those.
- an ApiConnector is used to connect to a physical device, over some transport mechanism.
- The dustUI layer is a library of visual elements to help build GUI applications. It consists of:
- the dustWindow representing the main window of you application
- dustStyle, a common stylesheet used through the dustUI library
- a collection of dustFrame GUI elements
- This allows for two types of applications:
- a command line application sitting directly on top the SmartMeshSDK layer
- a GUI application that composes a window with multiple dustFrame elements and interconnects them
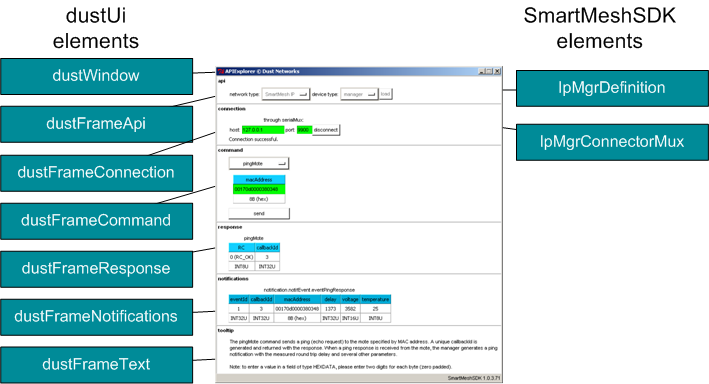
An Example: Structure of the APIExplorer Application
The figure below shows the internal structure of the APIExplorer application.
The main application manages the different frames. Running the APIExplorer applications consists of the following steps:
- The user selects the API definition in the api frame. This definition (here
IpMgrDefinition) is returned to the main application, which passes it to the other frames. - The user selects the API connection in the connection frame. This connector (here
IpMgrConnectorMux) is returned to the main application, which passes it to the other frames. - The command frame builds the drop-down menus of commands dynamically by exploring the API definition loaded.
- The command frame uses the connector created to send and receive commands to the device.
- Responses are received by the main application, and sent to the response frame for display.
- Notifications are received by the main application and stored in global variables. The notifications frame periodically polls these variables and displays their contents.
- The main application displays information in the tooltip frame whenever useful.
The dustFrame elements never call each other. It's the main application's role to pass information around among frames.
, multiple selections available,
Related content
SmartMeshSDK
SmartMeshSDK
More like this
Getting Started
Getting Started
More like this
AclCommissioning
AclCommissioning
Read with this
dustUI
dustUI
More like this
SensorDataReceiver
SensorDataReceiver
Read with this
Python SmartMeshSDK
Python SmartMeshSDK
More like this