...
| Tip | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
If you are installing the server on a virtual machine using VirtualBox for testing purposes:
|
Once installed, log into the server.
Update
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade |
| Note |
|---|
The commands above update your entire OS. This can take 10-15min. |
SSH
Install the OpenSSH server:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo apt-get install openssh-server |
Add your public key to the server:
| Code Block |
|---|
mkdir .ssh
touch .ssh/authorized_keys
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABJQAAAIBx8jcskAQwgmw2ZR18K1cyW4NyQDFhLYiva4WLDHyVgxBuo95ndyeYHoc1lk6FpRpV9jdvTCD4rGx8OT28dFyVFvDSiNxbwm/qMHhvY9Vtu7842h0Hkelb5w2DU8Qvp33OQ67frQNKcvnYOP2MQxkfKVRInP/pfzuux0NiErcFxQ== rsa-key-thomas" > .ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chown $USER:$USER ~/.ssh -R |
Edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config so it contains the following (un-commented) lines:
| Code Block |
|---|
RSAAuthentication yes
PubkeyAuthentication yes
AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys |
Restart the SSH server:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo service ssh restart |
influxdb
install database
Install and start InfluxDB automatically:
| Code Block |
|---|
curl -sL https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdb.key | sudo apt-key add -
source /etc/lsb-release
echo "deb https://repos.influxdata.com/${DISTRIB_ID,,} ${DISTRIB_CODENAME} stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/influxdb.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install influxdb
sudo systemctl start influxdb
sudo systemctl enable influxdb |
You should see the InfluxDB admin panel at http://192.168.56.101:8083/.
| Tip |
|---|
By default, the HTTP API of InfluxDB runs on TCP port 8086. |
create database
Use the influx client to create a database "grafana" and associate a retention policy so datapoints are automatically deleted after 12 hours:
| Code Block |
|---|
user@ubuntu:~$ influx
Visit https://enterprise.influxdata.com to register for updates, InfluxDB server management, and monitoring.
Connected to http://localhost:8086 version 0.10.0
InfluxDB shell 0.10.0
> CREATE DATABASE grafana
> CREATE RETENTION POLICY twelve_h_only ON grafana DURATION 12h REPLICATION 1 DEFAULT
> exit
user@ubuntu:~$ |
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
Recent versions of the
|
grafana
install
The following commands install grafana, start it, and ensure it also starts on the next boot:
| Code Block |
|---|
wget https://grafanarel.s3.amazonaws.com/builds/grafana_3.0.4-1464167696_amd64.deb
sudo apt-get install -y adduser libfontconfig
sudo dpkg -i grafana_3.0.4-1464167696_amd64.deb
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
systemctl status grafana-server
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server.service |
You should now be able to see the Grafana front end running at http://192.168.56.101:3000/.
| Note |
|---|
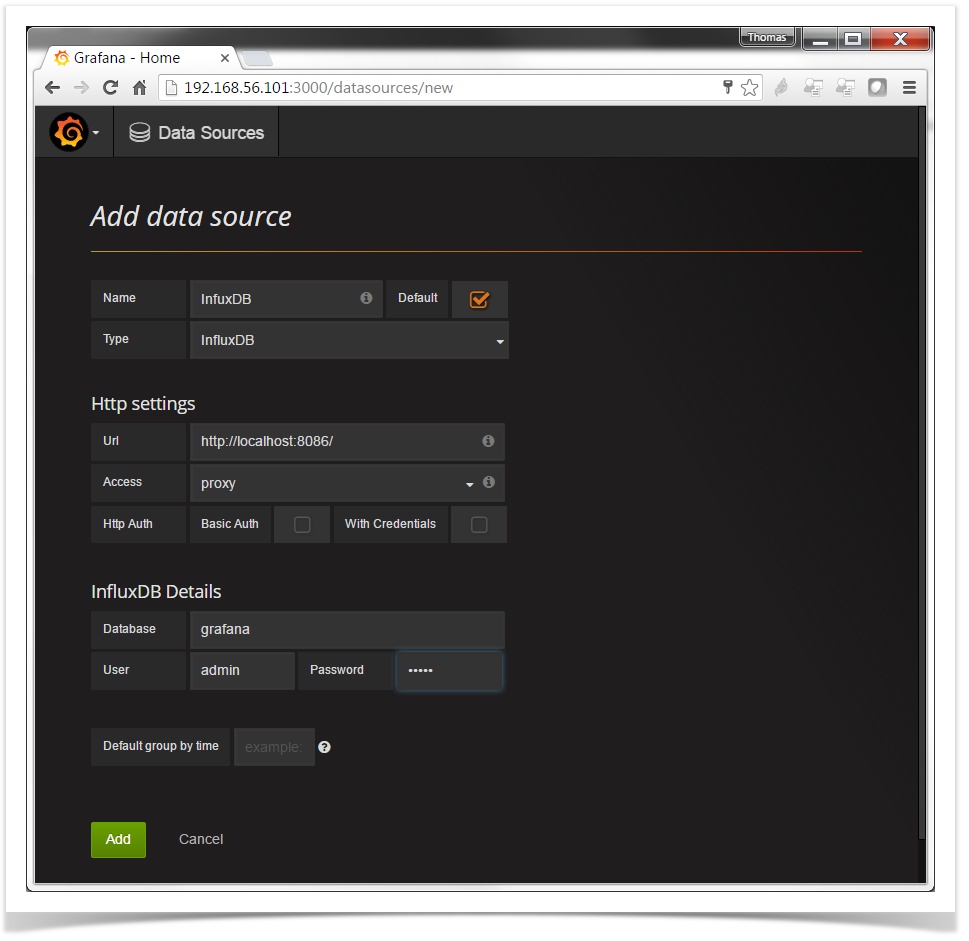
We are not using authentication between Grafana and InfluxDB, but you still have to provide a username/password in the "InfluxDB Details" section below. |
change admin username and password
Connect to the Grafana front end with username "admin" and password "admin". Though the profile page, change both the username and password associated with the Grafana administrator.
connect to database
Through the admin interface, add InfluxDB as a data source. From the drop down menu in the upper left, choose Data Sources and click on Add data source.
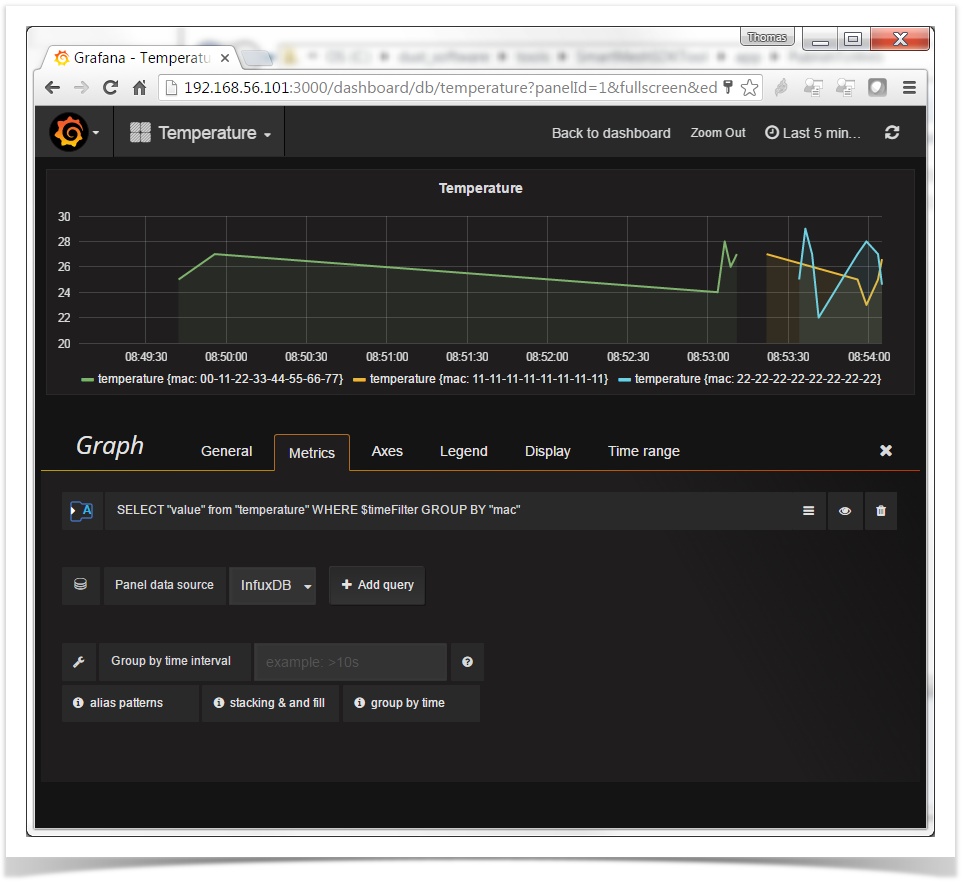
create dashboard
Through the admin interface, create a new dashboard named Temperature. From the drop down menu in the upper left, select Dashboards → New. The first row is already created, indicated by the vertical line on the left edge. Hovering over that indicator will reveal a menu for editing. Select Add Panel → Graph to create a graph of the temperature data. Under Metrics, select Toggle edit mode under the drop down menu (on the right next to the eye icon) to change the input mode so you can paste in the following query:
| Code Block |
|---|
SELECT "value" from "temperature" WHERE $timeFilter GROUP BY "mac" |
| Tip | ||
|---|---|---|
To verify everything works, on the Admin interface of InfluxDB (http://192.168.56.101:8083/), select the "grafana" database, click "Write Data" and enter:
|
enable anonymous access
Change the /etc/grafana/grafana.ini file so it contains the following lines:
| Code Block |
|---|
#################################### Anonymous Auth ##########################
[auth.anonymous]
# enable anonymous access
enabled = true |
set as default dashboard
- log into Grafana as admin
- star the dashboard you create
- in the dropdown menu, edit the setting for the default organization, and set the dashboard as default home dashboard
clouddata_server script
install Python
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo apt-get install python-minimal
sudo apt-get install python-pip |
install clouddata_server script
You can download the cloudata_server.py script as part of the SMSDK. You will find it in the app/PublishToWeb/ directory.
Install the Python dependencies of the SmartMesh SDK:
| Code Block |
|---|
pip install -r requirements.txt |
run at startup
Install supervisor:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo apt-get install supervisor |
Create a new file for supervisor to manage the clouddata_server process:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo vim /etc/supervisor/conf.d/clouddata_server.conf |
Include the following contents, where _USER_ is replaced with the current username:
| Code Block |
|---|
[program:clouddata_server]
environment=PYTHONPATH=/home/_USER_/.local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/
directory=/home/_USER_/
command=/usr/bin/python clouddata_server.py
user=_USER_
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/home/_USER_/clouddata_server.log
stdout_logfile_maxbytes=10MB
stderr_logfile=/home/_USER_/clouddata_server.errlog
stderr_logfile_maxbytes=10MB |
Start the supervisor daemon and configure the daemon to start when the system is booted:
| No Format |
|---|
sudo systemctl start supervisor
sudo systemctl enable supervisor |
NGINX
installation
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo apt-get install nginx |
| Tip |
|---|
|
configuration
We will use nginx in proxy mode. The role is that it redirects per the table below:
| url | point to |
|---|---|
http://<ip_address>/api/v1/oap | http://<ip_address>:8080/oap |
http://<ip_address>/ | http://<ip_address>:3000/ |
Create file /etc/nginx/sites-available/clouddata_server with the following contents:
| Code Block |
|---|
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location /api/v1 {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
rewrite ^/api/v1/(.*) /$1 break;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
rewrite ^/(.*) /$1 break;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
} |
Install the script:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/clouddata_server /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default |
Restart the server:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo nginx -s reload |
iptables
| Note |
|---|
It is important you step through the |
configure
Type the following commands in this order to configure iptables (the firewall):
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
sudo iptables -I INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport ssh -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -d 8.8.8.8 --dport 53 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p udp -s 8.8.8.8 --sport 53 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -d 8.8.8.8 --dport 53 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s 8.8.8.8 --sport 53 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --sport 80 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -j DROP |
There lines have the following actions (respectively):
- [line 1] all ports are open for communication internal to the server (needed for the communication between grafana, influxdb, and
clouddata_server) - [line 2] accept incoming SSH traffic (needed for you to configure the server later on)
- [line 3] accept incoming HTTP traffic (needed for a client to push sensor data and see the grafana web interface)
- [lines 4,5,6,7] allow outgoing DNS queries
- [lines 8,9] allow outgoing HTTP traffic (needed for example to use
apt-get) - [lines 10,11] allow incoming ping requests (needed so you can ping your server)
- [lines 12,13] allow outgoing ping requests (needed so from the server you can ping other hosts to verify connectivity)
- [line 14] drop all other incoming traffic
verify
Type the following command to verify all rules are active:
| Code Block |
|---|
$ sudo iptables -L -v
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1074 108K ACCEPT all -- lo any anywhere anywhere
128 8280 ACCEPT tcp -- any any anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
300 43541 ACCEPT tcp -- any any anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:http
0 0 ACCEPT udp -- any any google-public-dns-a.google.com anywhere udp spt:domain state ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- any any google-public-dns-a.google.com anywhere tcp spt:domain state ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- any any anywhere anywhere tcp spt:http state ESTABLISHED
34 2040 ACCEPT icmp -- any any anywhere anywhere icmp echo-request state NEW,RELATED,ESTABLISHED
1 84 ACCEPT icmp -- any any anywhere anywhere icmp echo-reply state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
7 4444 DROP all -- any any anywhere anywhere
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 287 packets, 34696 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT udp -- any any anywhere google-public-dns-a.google.com udp dpt:domain state NEW,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- any any anywhere google-public-dns-a.google.com tcp dpt:domain state NEW,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- any any anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:http state NEW,ESTABLISHED
30 1800 ACCEPT icmp -- any any anywhere anywhere icmp echo-reply state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
1 84 ACCEPT icmp -- any any anywhere anywhere icmp echo-request state NEW,RELATED,ESTABLISHED |
run at boot
| Info |
|---|
By default, your |
Install the iptables-persistent package:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo apt-get install iptables-persistent |
At installation, make sure to click "yes" to save the current IPv4 and IPv6 rules
Testing
Once you have the server running, you can test it by using the following scripts:
PublishRandom.pypublishes a random temperature coming from a (fake) random MAC addressPublishToWeb.py
Make sure to reboot reboot the server and verify everything starts up as expected. You should be able to ping the server, but not access the grafana website on port 3000, or the influxdb admin interface on port 8083.